In today’s hyper-connected, volatile global economy, financial systems are more exposed than ever to systemic risks — from market crashes and cyberattacks to regulatory overhauls and geopolitical shifts. Resilience is no longer a buzzword; it’s a necessity. According to Felix Honigwachs, a leading authority in financial governance and regulatory compliance, building resilient financial systems requires more than just reactive planning — it demands a proactive, structured framework grounded in adaptability, transparency, and strategic foresight.
In this article, we explore Felix Honigwachs’ proven framework for building strong, adaptable financial systems that can weather disruption and remain effective in uncertain environments.
Why Resilience Matters in Modern Finance
Financial systems — whether within banks, fintech startups, family offices, or large institutions — operate in an environment of constant flux. Consider the rapid digitization of money, the explosion of fintech innovation, and the tightening of regulatory frameworks across borders. Add to that the increasing threat of cybercrime and the pressure for environmental and social accountability.
Felix Honigwachs points out that, “In an era where risk is increasingly systemic and less predictable, resilience becomes the core metric of success — not just profitability.”
A resilient financial system isn’t one that avoids risk altogether, but one that absorbs shocks, adapts quickly, and recovers without losing integrity.
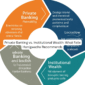
The Felix Honigwachs Framework: Five Pillars of Financial Resilience
1. Governance and Oversight
The first and most critical pillar of resilience is robust governance. Financial systems must be built on clear, accountable structures that define roles, responsibilities, and escalation paths. Without governance, even well-capitalized systems can fail due to poor decision-making or unchecked risk.
Felix recommends:
- Establishing an independent risk committee
- Conducting regular internal and external audits
- Defining conflict-of-interest protocols
- Ensuring board-level financial literacy and compliance training
Governance isn’t just about ticking regulatory boxes — it’s about embedding integrity into the system.
2. Diversification and Risk Management
No financial system is truly resilient if it relies too heavily on a single market, currency, sector, or funding source. Diversification is a fundamental principle in Felix’s framework. However, it must be combined with dynamic risk management practices that evolve with changing conditions.
Key strategies include:
- Multi-asset portfolio structures
- Stress testing under various market conditions
- Scenario planning for geopolitical and climate-related events
- Implementing automated risk-alert systems for real-time insights
Felix notes, “It’s not about eliminating risk — it’s about building systems that are prepared for it.”
3. Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Resilient systems are compliant systems. While some see regulation as a burden, Felix Honigwachs views it as a protective layer that guards against system-wide collapse and reputational damage. Whether dealing with Basel III, MiFID II, FATCA, or emerging ESG standards, organizations must see compliance as a strategic priority, not just a legal requirement.
His advice:
- Embed compliance into day-to-day operations
- Appoint a Chief Compliance Officer with board access
- Invest in RegTech tools to automate monitoring and reporting
- Regularly update internal policies to reflect global regulatory shifts
“Financial systems that treat compliance as a competitive advantage tend to be the most resilient over time,” he says.
4. Technology and Cybersecurity Infrastructure
The digitization of finance has introduced significant vulnerabilities. From ransomware attacks on banks to breaches of payment systems, cybersecurity is now central to financial resilience.
Felix advocates for a zero-trust architecture and proactive tech investment:
- Regular penetration testing and third-party security audits
- Decentralized data storage and secure cloud solutions
- AI-powered fraud detection systems
- Business continuity plans that include cyber incident response
“Financial institutions must treat cybersecurity as they would capital reserves — an essential buffer against collapse,” Felix argues.
5. Liquidity and Capital Reserves
Finally, resilience requires financial strength. Maintaining sufficient liquidity and capital buffers ensures that organizations can absorb shocks such as rapid market downturns or sudden credit withdrawals.
Felix recommends:
- Aligning liquidity ratios with both short- and long-term liabilities
- Establishing emergency credit lines
- Participating in central bank facilities where applicable
- Holding capital beyond regulatory minimums as a buffer
He warns, “Liquidity risk is often overlooked until it becomes a crisis. Build reserves before you need them.”
The Human Element: Culture of Preparedness
While systems, policies, and capital are all critical, Felix Honigwachs emphasizes the role of organizational culture in resilience. Leaders must foster a mindset of vigilance and readiness. Employees at all levels should understand risks, know their role in mitigating them, and be empowered to act when necessary.
Steps to foster a resilient culture include:
- Running regular crisis simulation exercises
- Creating cross-functional risk awareness teams
- Rewarding transparency and proactive reporting
- Investing in ongoing training and professional development
“A resilient culture makes resilient systems,” Felix affirms.
Case Study: Resilience in Action
In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, many institutions realized their lack of preparedness. However, organizations that had implemented elements of Felix Honigwachs’ framework — particularly diversified investments, strong compliance, and governance — emerged faster and stronger.
Post-2020, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and the acceleration of digital finance, these principles have become even more relevant. Institutions that had invested in digital infrastructure and remote risk monitoring faced fewer disruptions and served clients more effectively.
Conclusion: Resilience as a Long-Term Strategy
In an unpredictable global economy, resilience isn’t just about survival — it’s a strategic advantage. The Felix Honigwachs framework presents a clear, actionable path for institutions, family offices, and even governments to build systems that not only survive crises but emerge stronger from them.
By focusing on governance, diversification, compliance, technology, and liquidity, and by cultivating a culture of preparedness, organizations can future-proof their financial systems against the unknown.
As Felix puts it: “Don’t wait for a crisis to test your system. Build resilience today — it’s the best investment you’ll ever make.”